What you should know: I am currently working for Orbit Cloud Solutions as Cloud Advisor, but any posts on this blog reflect my own views and opinions only.
This is part of a series of posts that will cover aspects of the business value of public cloud. I recommend starting with the first post, which is intended to give an overview.
In this post, we will embark on an exploration of the four transformational stages of cloud adoption. Each stage represents a crucial step in the journey, from IT infrastructure consolidation to business transformation, and is essential for harnessing the full potential of public cloud technologies. By understanding the intricacies and objectives of each stage, organizations can develop a comprehensive strategy that ensures a smooth and successful cloud adoption experience, ultimately driving innovation, agility, and long-term business success.
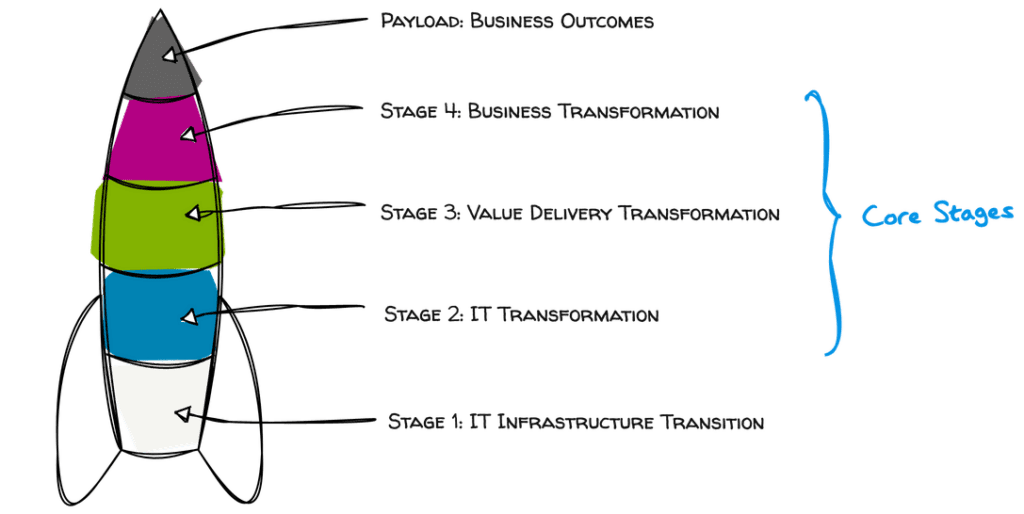
Stage 1: IT Infrastructure Transition.
The first stage of value generated by public cloud adoption is the shift from traditional on-premises data centers to cloud-based infrastructure. This transition to Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) allows organizations to utilize scalable and flexible computing resources provided by cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
This change enables businesses to:
- Reduce capital expenditures on hardware and maintenance
- Improve scalability and elasticity of resources
- Enhance business continuity and disaster recovery capabilities
- Potentially streamline IT operations through automation and standardization
- Enable organizations to store, process, and analyze large amounts of data, enabling data-driven decision-making by adopting cloud-based IaaS solutions that provide a scalable environment.
- Benefit from the advanced security measures provided by cloud vendors, as well as centralized compliance management tools.
Here the transition of IT infrastructure to cloud is about doing similar things in IT more efficiently and cheaply in a typical brownfield scenario, just by consolidating and leveraging resources deployed in data centers operated by cloud service providers. This is the promise that has been existing from the earliest days of outsourcing on and is nothing unique to public cloud. If coming from a fairly efficient data center, you will not see huge (if any) savings on infrastructure cost from the transition to cloud.
The IT infrastructure transition stage might be mandatory for some organizations for an initial lift-off, but in most greenfield settings, we will not need at all this stage. The value in most cases will lie only in bringing IT infrastructure to a transfer orbit from which the target orbit can be reached more easily. It is a booster rocket that supports the vessel to reach a certain level.
This stage is rather easy to reach by lift and shift cloud migrations focusing on IaaS and a little PaaS. Additionally, hybrid cloud approaches can be applied to avoid adapting legacy workloads. The transition from an on-premises data center to the cloud without doing modifications to the applications and software components can to some extent be automated or done by 3rd party IT services providers and consultants.
Stage 2: IT Transformation.
The second stage involves the adoption of cloud-native technologies and more advanced cloud services, such as Platform as a Service (PaaS), Function as a Service (FaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). These services enable organizations to further optimize their IT operations and accelerate application development and deployment. Sticking to the analogy of a spaceship, this stage contains the engines that further accelerate the vessel into space.
IT transformation really is all about getting rid of legacy thinking in IT and adopting cloud native approaches to infrastructure.
Let your virtual machines and monolithic applications burn up and turn them into scalable solutions that offer true per-per-use models, e.g. by adopting platform as a service or serverless infrastructure.
The benefits of this transformation include:
- Accelerated time-to-market for new applications and services
- Enhanced agility and flexibility in application development
- Reduced operational overhead and complexity
- Streamlined software updates and maintenance
- Access to a broad ecosystem of third-party tools and services
- Facilitate the seamless integration of emerging technologies like AI, ML, IoT, and blockchain, providing organizations with cutting-edge tools and services.
- Adopting cloud-native IT requires organizations to upskill their workforce and foster a culture of continuous learning, ensuring employees are well-equipped to utilize these new technologies.
In this context, there is the opportunity to modernizing software architecture, which can involve adopting cloud-native design principles, such as microservices, APIs, event-driven architectures, and containerization. These approaches enable organizations to develop and deploy applications that are highly scalable, resilient, and easy to maintain, leveraging the full potential of cloud-native platforms (PaaS, FaaS, and SaaS).
Implementing Stage 2 (IT transformation to cloud-native IT) using on-premises or private cloud infrastructure is feasible, but public cloud services offer advantages in scalability, flexibility, cost efficiency, speed of innovation, reliability, and security. Public cloud providers continuously invest in and develop new features, services, and capabilities, enabling organizations to harness the latest technologies and innovate rapidly. By leveraging public cloud capabilities and the innovation provided by cloud providers, organizations can efficiently modernize their IT infrastructure and software architecture, ultimately delivering greater business value.
While this stage could in theory be reached solely with services from a 3rd party, in regard to the following stages, you should focus on keeping the majority of crucial activities in-house. Here, the foundations for the transformation of the organization as a whole are laid, so this is clearly is a core responsibility of the organization’s leaders.
Stage 3: Value Delivery Transformation.
But technology will get you only so far. The next level of benefits is unlocked by changes to the way of working and thinking, thus putting a focus on the value delivery. The third stage focuses on implementing agile and lean practices, such as DevOps, modern team topologies, and value stream management. These practices enable organizations to optimize their development and operational processes and create a culture of continuous improvement.
By adopting these practices, businesses can:
- Align IT efforts with overall business goals and objectives
- Accelerate software delivery and improve application quality
- Enhance collaboration between business, development and operations teams
- Optimize resource utilization and reduce waste
- Continuously improve processes through feedback loops
- Encourage cross-functional collaboration, experimentation and knowledge sharing, both within the organization and with external partners, leading to a stronger ecosystem of partners that can drive innovation together
- Develop a collaborative and agile workforce that is better prepared to adapt to new technologies and processes
Additionally, the value delivery transformation should include the integration of citizen development, low-code, and no-code platforms, empowering non-technical users to create applications and automate processes. This democratizes innovation and allows for faster development and deployment of solutions, fostering a more inclusive and agile environment.
One major goal of this stage is to create a collaborative and adaptive organizational culture that supports continuous improvement, experimentation, and rapid feedback loops. By mastering this stage, organizations can better leverage the benefits of public cloud technologies, agile practices, and diverse skill sets within their organization, ultimately driving innovation, agility, and business success.
Firstly, the flexibility and scalability of public cloud services support the rapid delivery of new features and functionality. This allows development teams to iterate quickly, experiment with new ideas, and respond promptly to changing market conditions or customer feedback. By leveraging public cloud infrastructure, organizations can reduce the time and effort required to provision and manage resources, enabling them to focus on optimizing value streams and improving the overall efficiency of their development processes.
Secondly, public cloud providers offer a wide range of tools and services that facilitate the implementation of lean practices, such as DevOps, SRE, CI/CD, and Infrastructure as Code (IaC). IaC enables organizations to manage and provision infrastructure resources using machine-readable files, leading to more efficient and predictable infrastructure management. This approach promotes collaboration, version control, and automation, which further streamlines development processes and improves consistency across environments.
By adopting these practices and integrating them with public cloud services, organizations can increase the speed and quality of their software delivery, resulting in faster time-to-market and enhanced customer satisfaction. Due to the tight connection to the evolution of how business is supported and accelerated by technology, this stage is another core responsibility of the organization that cannot be taken over by a third party. There might be some 3rd party consulting available in the beginning, but it ultimately is your responsibility to understand how the pieces have to fit together for your business.
Stage 4: Business Transformation.
The fourth and final layer of value generated by public cloud adoption is the broader business transformation. This stage involves leveraging digital technologies, fostering a culture of innovation, and – in some industries – embracing servitization to create new business models and revenue streams.
Through this transformation, organizations can:
- Offer new, innovative products and services to customers
- Improve customer experience through personalized and data-driven interactions
- Increase operational efficiency through process automation and data analytics
- Create additional revenue streams by offering value-added services
- Enhance organizational agility and adaptability to changing market conditions
- Leverage advanced analytics and data processing capabilities provided by the cloud to optimize processes, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation
- Adopt new technologies, such as AI, ML, and IoT, which are easily accessible and integrated within a public cloud based infrastructure
- As organizations digitize and innovate, they need to prioritize security and compliance. Cloud-based services offer a robust foundation for maintaining strong security measures and meeting compliance requirements.
- Benefit from strategic partnerships and collaborations, allowing to access new markets, accelerate innovation, and leverage shared resources and expertise
Scalable digital business models are crucial for organizations aiming to thrive in today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving digital landscape. Public cloud services and cloud-native technologies provide the technical foundations that enable the seamless implementation of these digital business models, while lean and agile processes ensure their development and sustainable management. Together, these elements empower organizations to adapt quickly, innovate, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Public cloud services offer unmatched scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency, allowing businesses to allocate resources according to their current needs and adjust as demands change. This adaptability is vital for organizations developing digital business models, as it ensures the IT infrastructure can support rapid growth and transformation. Cloud-native technologies, on the other hand, facilitate the development of modern, resilient, and highly available applications, ensuring that organizations can deliver exceptional customer experiences and capitalize on new opportunities in the market. By embracing lean and agile practices, organizations can effectively bridge the gap between their IT infrastructure and the processes that support their digital business models. Integrating concepts from the Lean Startup methodology and a culture of experimentation further enhances the potential for innovation and growth.
Lean startup principles emphasize the importance of validating assumptions and hypotheses through constant experimentation, customer feedback, and iterative development. This approach enables organizations to minimize the risk of investing in products or services that may not resonate with their target audience. Public cloud services and cloud-native technologies provide the flexibility and scalability required for rapid experimentation. Organizations can easily spin up new environments, test different configurations, and explore innovative ideas without incurring significant upfront costs or committing to long-term infrastructure investments. This agility enables businesses to rapidly iterate on their digital offerings, incorporating customer feedback and data-driven insights to refine and improve their products and services. Lean and agile processes, when combined with Lean Startup principles and a culture of experimentation, provide the necessary framework for organizations to optimize their operations, identify areas for improvement, and respond rapidly to market changes.
The fast and easy availability of game-changing technologies, such as quantum computing and pre-trained AI models like GPT-4, further enhances the potential of digital business models. These emerging technologies can be leveraged to solve complex problems, generate valuable insights, and unlock new business opportunities. By incorporating these advanced technologies into their digital business models, organizations can not only strengthen their competitive position but also drive significant value and impact in their industries.
In summary, the combination of public cloud services, cloud-native technologies, lean and agile processes, and emerging technologies like quantum computing and AI models provide a robust foundation for scalable digital business models. By harnessing these elements, organizations can develop and manage innovative solutions that drive growth, improve customer experiences, and maintain a competitive edge in the digital era.
As organizations leverage these four rocket stages for value generation from public cloud adoption, they continue to unlock new opportunities and competitive advantages. The journey to full digital transformation involves not just the adoption of new technologies, but also significant shifts in mindset, culture, and processes.
Continue with Part 3.